Bull Spread Call Option Strategy Explained Clearly | 2026

Bull Spread Call Option Strategy: How to Trade “Moderately Bullish” Markets (Smart & Professional Way)
You think the market is going up.Your gut says “Buy a Call Option.”
But then you remember the last time you bought a naked Call—the market did go up, but slowly. Theta (Time Decay) ate all your profits, and you still ended up with a loss.
This is one of the most common mistakes option buyers make.
Being directionally right is not enough in options trading.
This is exactly where the Bull Spread Call option trading strategy comes in. It is the smart, structured way to trade bullish markets without letting time decay destroy your capital.
What Is a Bull Call Spread?
A Bull Call Spread is a bullish options strategy where a trader buys a call option at a lower strike price and sells another call option at a higher strike price with the same expiry to reduce cost and limit risk.
A Bull Call Spread (also called a Bull Call Debit Spread or bull spread call option) is a two-leg option strategy used when you expect the market to go up, but you don’t expect it to go to the moon immediately.
It Involves
- Buying a Call Option (lower strike)
- Selling a Call Option (higher strike)
- Both options must have the same expiry date
The Logic
- The Call you buy benefits from an upward move
- The Call you sell reduces the cost of the trade
- Lower cost = lower risk + lower breakeven
This is why the bull call spread option strategy is preferred by professionals.
Why the Bull Spread Call Option Strategy Works
Most option buyers lose money because:
- Time decay works against them
- Volatility collapses after entry
- The market moves slower than expected
The bull spread call option strategy solves these problems by:
- Reducing upfront premium
- Lowering breakeven
- Softening theta decay
- Increasing probability of profit
You are not chasing lottery profits.You are trading probability and structure.
Bull Call Spread Strategy Setup (Nifty Example)
Let’s say Nifty is trading at 26,135 and you expect it to reach 26,300 by expiry.
The Trade
- Buy: 26,135 CE (ATM) at ₹150
- Sell: 26,300 CE (OTM) at ₹60
The Math
- Premium Paid: ₹150
- Premium Received: ₹60
- Net Debit (Cost): ₹90
Instead of paying ₹150 for a naked Call, you only paid ₹90.
👉 This immediately reduces your risk and lowers your breakeven point.
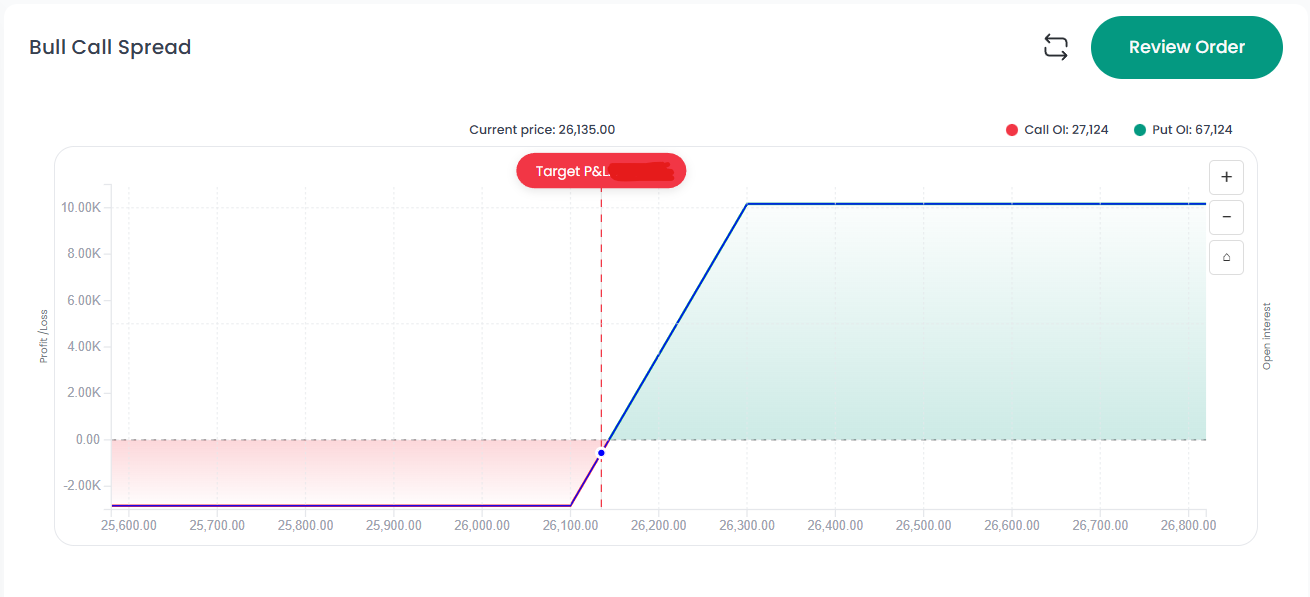
Risk vs Reward Profile of Bull Call Spread
This is a Limited Risk, Limited Reward strategy.
Maximum Loss
- Limited to Net Debit
- In this example: ₹90 per lot
- Even if Nifty crashes to 25,000, you lose only ₹90
Maximum Profit
Formula:
(Strike Width) – Net Debit
- Strike difference = 165 points
- Net Debit = ₹90
- Max Profit = ₹75 per lot
Breakeven Point
Lower Strike + Net Debit
- 26,135 + 90 = 26,225
You start making money as soon as Nifty crosses 26,225.
When Should You Use a Bull Call Spread?
Do not use this strategy blindly.
Use It Only When
- View is Moderately Bullish(You expect 200–300 points, not 1000 points)
- Implied Volatility is High(Naked calls are expensive)
- You Are Close to Expiry(Theta decay is aggressive)
The sold call loses value faster, which actually helps your spread.
Why Bull Call Spread Is Better Than Buying a Naked Call
Professional traders prefer consistency over jackpots.
How to Execute Bull Call Spread on Firstock
- Open Strategy Builder
- Select expiry (weekly or monthly)
- Buy the ATM Call
- Sell the OTM Call
- Always execute the Buy leg first
⚠️ Since this is a Debit Strategy, margin is usually limited to the premium paid.Selling first may trigger margin requirements—avoid that mistake.
Strike Selection Masterclass: Which Strikes to Pick?
1. Conservative Setup (High Win Rate)
- Buy ITM Call
- Sell ATM Call
- Higher cost, lower ROI, better sleep
2. Standard Setup (Balanced)
- Buy ATM Call
- Sell OTM Call
- Best risk–reward balance
3. Aggressive Setup (High ROI)
- Buy OTM Call
- Sell far OTM Call
- Cheap but low probability
Your strike selection determines whether you survive long term.
Bull Call Spread vs Bull Put Spread
Rule of Thumb
- Low IV → Bull Call Spread
- High IV → Bull Put Spread
The 50% Exit Rule (Professional Trader Secret)
Professional traders rarely hold till 3:30 PM on expiry day.
Why?
- Gamma risk increases sharply
- Small moves cause huge P&L swings
Smart Exit Rule
- Exit at 50–75% of max profit
- Don’t be greedy for the last rupee
Adjustments: What If the Market Falls?
Option 1: Do Nothing
- Max loss already defined
- Let probability play out
Option 2: Advanced Adjustment
- Convert into a Long Call Butterfly
- Reduces loss but requires experience
Conclusion: Trade Safer, Trade Smarter
The bull spread call option strategy is the backbone of consistent options trading.
It:
- Protects capital
- Reduces emotional trading
- Improves probability
- Forces risk discipline
Next Action Step
Open the option chain:
- Compare ATM Call cost
- Compare Bull Call Spread cost
- See how much cheaper and smarter spreads really are
FAQs
1. How much margin is required for a bull call spread?
Since this is a debit strategy, you usually need only the net premium paid. Margin issues arise only if you sell first.
2. Can I profit if the market stays flat?
No. You need price to cross the breakeven point. However, losses are much smaller than naked calls.
3. What if the market shoots far above my sold strike?
Your profit is capped. This is the cost of safety.
4. Is bull call spread good for beginners?
Yes. It is one of the safest directional strategies due to predefined risk.
5. Can bull call spread be traded intraday?
Yes, but it works best as a positional strategy (2–5 days).
6. Which index is best for bull call spread?
Nifty, Bank Nifty, and Fin Nifty due to high liquidity.
7. Can I hold bull call spread till expiry?
Yes, but professional traders prefer early exits to avoid gamma risk.
8. How do I close the trade?
You must exit both legs simultaneously. On Firstock - Option Trading App , use the "Exit Basket" or select both positions and click "Square Off" to ensure you don't leave one leg open (which would expose you to naked risk)
Disclaimer
This content is strictly for educational purposes only and should not be considered investment or trading advice. Options trading involves significant risk. Consult a registered financial advisor before trading.





