Understanding Strategies and F&O (Futures and Options) in Trading
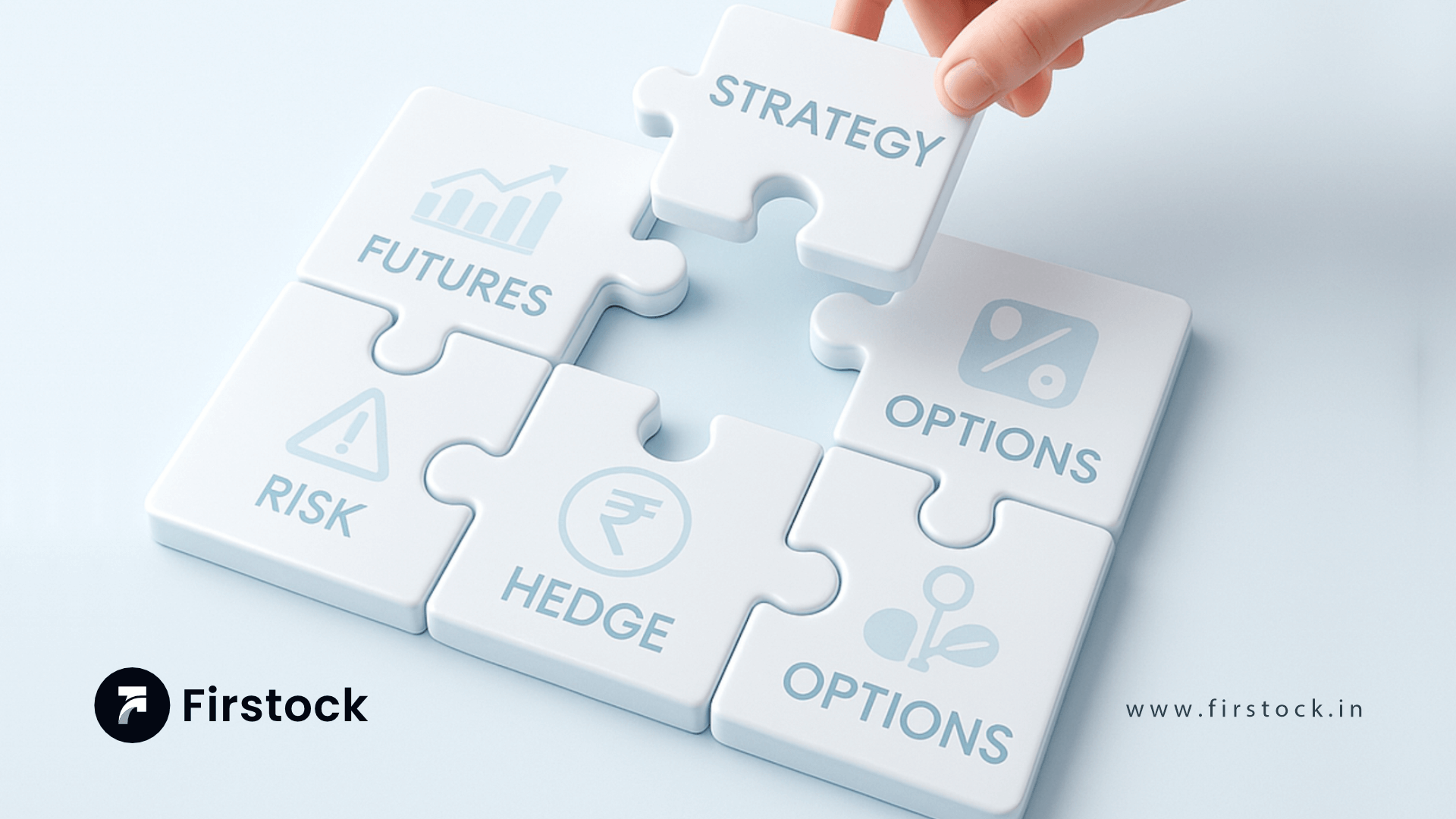
In the world of financial markets, strategies and F&O (Futures and Options) are essential concepts that traders use to plan and execute trades effectively. Here’s a detailed explanation of what these terms mean and how they interplay in trading.
What Are Trading Strategies?
A trading strategy is a systematic plan that traders use to make decisions about buying and selling assets in the market. It is based on predefined rules and analysis to identify favorable market conditions and price points for entering or exiting trades. Strategies help traders avoid emotional decisions and maintain consistency.
There are several types of trading strategies, broadly categorized into:
Technical strategies:
These rely on technical indicators and price patterns to predict market movements. Examples include trend trading (following the direction of price momentum), scalping (making many quick trades to capture small price moves), and swing trading (holding positions for days or weeks to profit from medium-term trends).
Fundamental strategies:
These involve analyzing economic indicators, company financials, and other fundamental data to determine the intrinsic value of an asset and trade accordingly.
Quantitative strategies:
These use complex mathematical models and multiple data points to identify trading opportunities and often involve automated trading systems.
A well-developed trading strategy includes risk management rules, such as stop-loss limits and position sizing, to protect capital and manage losses.
What is F&O (Futures and Options)?
Futures and Options (F&O) are types of financial derivatives that allow traders to speculate on the price movements of an underlying asset without owning it outright.
Futures contracts obligate the buyer to purchase, and the seller to sell, the underlying asset at a predetermined price on a specific future date. This means both parties have a binding commitment.
Options contracts give the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) the underlying asset at a predetermined price within a specified timeframe. The seller must honor the contract if the buyer exercises the option.
F&O trading is popular because it allows leverage - traders can control large positions with a relatively small margin, amplifying both potential profits and risks.
Popular F&O Strategies: Straddle, Strangle, and More
F&O trading involves a variety of strategies designed to profit from different market conditions, especially volatility. Two widely used options strategies are straddle and strangle:
Straddle:
This strategy involves buying or selling both a call option and a put option at the same strike price and expiry date. It is used when a trader expects significant price movement but is uncertain about the direction. The profit comes if the underlying asset moves sharply up or down beyond the total premium paid.
Strangle:
Similar to a straddle, a strangle involves buying or selling a call and a put option with the same expiry but different strike prices - the call option strike is higher, and the put option strike is lower than the current market price. This is generally a cheaper strategy than a straddle but requires a larger price move to be profitable.
Other common F&O strategies include:
Protective Put: Buying a put option to hedge against a potential decline in the underlying asset.
Covered Call: Holding the underlying asset while selling a call option to earn premium income.
Bull and Bear Spreads: Using combinations of options to profit from moderate price rises or falls while limiting Managing risk.
How to Plan and Execute F&O Trades
Successful F&O trading involves careful planning and analysis:
Research: Understand the underlying asset, market conditions, and derivative specifics like expiry and margin.
Margin management: Ensure adequate funds to meet margin requirements, which can fluctuate with the underlying asset’s price.
Market study: Analyze both the spot and derivative markets, considering macroeconomic and microeconomic factors affecting prices.
Strategy selection: Choose an appropriate futures or options strategy based on your market view and risk tolerance.
Trade execution: Use reliable trading platforms to place orders, keeping expiry and margin in mind.
Conclusion
Trading strategies provide a structured approach to navigating markets, helping traders make informed decisions and manage risks. Futures and Options (F&O) are powerful derivative instruments offering leverage and flexibility but require specialized strategies and risk controls. Incorporating strategies like straddles and strangles can help traders capitalize on market volatility, regardless of direction. Combining sound strategies with a deep understanding of F&O can enhance trading effectiveness and potential profitability.