What Is Bear Put Spread? Strategy, Example & Payoff | 2026

What Is Bear Put Spread? A Complete Guide to the Bear Put Spread Strategy
If you have a moderately bearish view on a stock or index—meaning you expect it to go down but not crash completely—buying a straight Put Option might seem expensive. This is where the Bear Put Spread strategy comes into play.
It is a popular defined-risk options strategy that allows traders to profit from a downward move while reducing the upfront cost of the trade.
What Is a Bear Put Spread?
A Bear Put Spread, also known as a bearish put spread or long put vertical spread, is a straightforward options strategy for traders who expect a stock or index to decline moderately.
Instead of buying a single Put option, the strategy involves two simultaneous actions:
- Buy one Put option at a higher strike price
- Sell another Put option at a lower strike price
That’s it—two legs working together.
Both options:
- Have the same expiry date
- Belong to the same stock or index
This combination creates a debit spread, meaning you pay a net premium to enter the trade—but much less than buying a naked Put.
Why Do Traders Use the Bear Put Spread Strategy?
The primary objective of a bear put spread strategy is cost reduction with controlled risk.
When you buy a naked Put:
- Premiums are expensive
- Time decay (Theta) works strongly against you
- You need a large price move to break even
With a bearish put spread:
- Selling the lower-strike Put generates premium
- That premium offsets the cost of the bought Put
- Risk and reward are clearly defined from day one
This makes the bear put spread ideal for:
- Volatile markets
- Earnings seasons
- Market corrections
- Traders who value risk control
How Does the Bear Put Spread Strategy Work?
To construct a bear put spread, you execute two transactions simultaneously:
1. Buy a Put Option (Higher Strike)
- Usually At-the-Money (ATM) or slightly In-the-Money (ITM)
- Gives you the right to sell at a higher price
- This leg benefits directly from falling prices
2. Sell a Put Option (Lower Strike)
- Typically Out-of-the-Money (OTM)
- Generates premium income
- Reduces overall trade cost
The Setup at a Glance
- Market View: Moderately Bearish
- Trade Type: Debit Spread (Net Debit)
- Leg 1: Buy Higher Strike Put
- Leg 2: Sell Lower Strike Put
This structure ensures:
- Limited loss
- Limited profit
- Higher probability of success than naked Put buying
Risk and Reward Profile of a Bear Put Spread
Understanding the payoff structure is essential before placing any options trade.
Maximum Loss (Limited)
- Equal to the Net Premium Paid (Net Debit)
- Occurs if the stock/index expires above the higher strike
- Both options expire worthless
👉 This is the biggest advantage of the bear put spread: you know your worst-case loss upfront.
Maximum Profit (Limited)
Formula:
Difference in Strike Prices – Net Premium Paid
- Achieved if price falls below the lower strike
- Profit is capped but predictable
Breakeven Point
Formula:
Long Put Strike Price – Net Premium Paid
If price closes at breakeven, the gain from the long Put exactly offsets the cost of the spread.
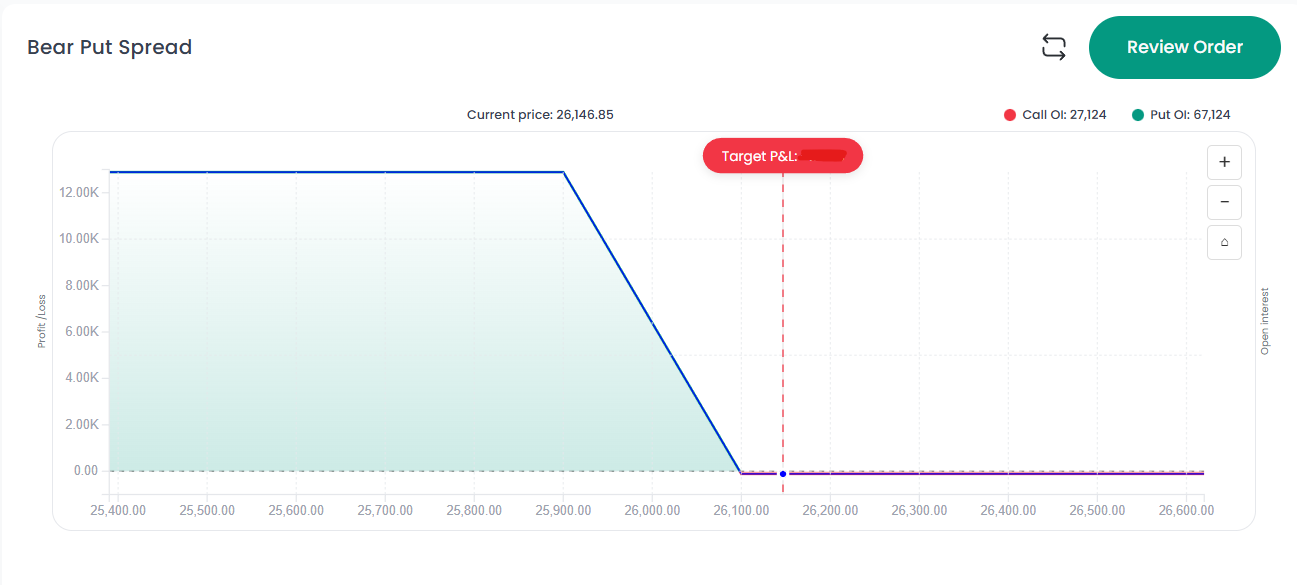
Example of a Bear Put Spread (Nifty 50)
Let’s assume Nifty 50 is trading at 26,146 and you expect it to fall to around 25,900, but you want to limit your risk.
Trade Construction
- Buy 26,100 PE (Higher Strike): Premium = ₹150
- Sell 25,900 PE (Lower Strike): Premium = ₹60
Net Debit (Cost of Trade)
₹150 – ₹60 = ₹90
Scenario Analysis
Scenario 1: Nifty stays above 26,100
- Both options expire worthless
- Loss = ₹90 (Maximum Loss)
Scenario 2: Nifty falls to 25,900 or lower
- Spread width = 200 points
- Profit = 200 – 90 = ₹110 (Maximum Profit)
Scenario 3: Nifty closes at 26,010 (Breakeven)
- Long Put gain = ₹90
- Net P&L = ₹0
Bear Put Spread vs Buying a Naked Put
Key Insight:A bear put spread sacrifices unlimited upside in exchange for better probability, lower cost, and controlled decay.
When to Use the Bear Put Spread Strategy?
Knowing how to construct the trade is easy. Knowing when to use it is what separates consistent traders from gamblers.
1. Moderately Bearish Outlook
You expect a decline—but not a crash.
2. High Implied Volatility (IV)
High IV makes naked Puts expensive.Selling the OTM Put offsets this cost.
3. Defined Target Price
You have a clear technical target or support level.You place the short strike at that level.
Impact of Options Greeks on a Bear Put Spread
Delta (Direction)
- Net negative Delta
- Gains value as price falls
- Less volatile than naked Put
Theta (Time Decay)
- Long Put loses value over time
- Short Put gains value over time
- Net result: reduced Theta damage
Vega (Volatility)
- Slightly long Vega
- IV crush impact is significantly lower than buying a single option
Managing a Bear Put Spread Trade
1. Profit Booking Strategy
Because profit is capped, there’s no need to hold till expiry.
Rule of Thumb:Exit when 75–80% of max profit is achieved.
This avoids last-day volatility and Gamma risk.
2. Stop-Loss Strategy
Exit the trade if:
- Price breaks key resistance
- Spread loses ~50% of net debit
Debit spreads decay fast when wrong. Hope is not a strategy.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Bear Put Spread
Advantages
- Lower cost than naked Put
- Defined and limited risk
- Better probability of profit
- Reduced Theta and IV impact
Disadvantages
- Capped profit
- Two-leg execution
- Less flexibility compared to single options
Conclusion: Is Bear Put Spread Worth Using?
A bear put spread is one of the smartest bearish strategies for traders who want:
- Lower capital requirement
- Predictable outcomes
- Better risk control
If you believe markets will fall gradually, not crash violently, this strategy fits perfectly into a disciplined F&O trading plan.
FAQs
1: Is a Bear Put Spread bullish or bearish?
A bear put spread is bearish. It works best when prices decline moderately.
2: What is the difference between Bear Put Spread and Bull Put Spread?
- Bear Put Spread: Debit spread, bearish view
- Bull Put Spread: Credit spread, bullish/neutral view
3: Can I lose more than what I paid?
No. Maximum loss is limited to the net premium paid.
4: Do I need margin to trade a Bear Put Spread?
No heavy margin is required. Only the net debit amount is needed.
5: When should I exit a Bear Put Spread?
- At 75–80% of max profit
- When price hits your target
- When stop-loss is triggered
6: Is Bear Put Spread better than buying a Put?
Yes when:
- Implied Volatility is high
- You expect a moderate decline
- You want reduced time decay impact
If you expect a sharp crash, naked Puts may perform better.
Disclaimer
This content is for educational purposes only and should not be considered investment or trading advice.





